HydroTrim® is a new product from Huvepharma containing both sulfadiazine (500 mg/g) and nanonised trimethoprim (100 mg/g). The nanonisation enables trimethoprim to stay in suspension, even at high concentrated stock solutions of medicated water.
Sulfonamides and sulfonamide/trimethoprim combinations are among the most frequently used antibiotics in veterinary medicine. These drugs are used to treat a variety of bacteria, protozoal and certain fungal infections. They are most effective in the early stages of infections when pathogens multiply rapidly.
Chemistry and mode of action
Sulfonamides are derivatives of sulfanilamides and are synthetically manufactured. Various sulfonamide products are therapeutically used in veterinary medicine with structural differences (sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole, sulfamethazine, others).
Sulfonamides interfere with the biosynthesis of folic acid in bacterial cells by preventing para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) from incorporating into the folic acid molecule.
Diaminopyrimidines (trimethoprim and others) also interfere with the biosynthesis of folic acid in bacterial cells. They prevent the conversion of dihydrofolic acid and tetrahydrofolic acid by competitive binding.
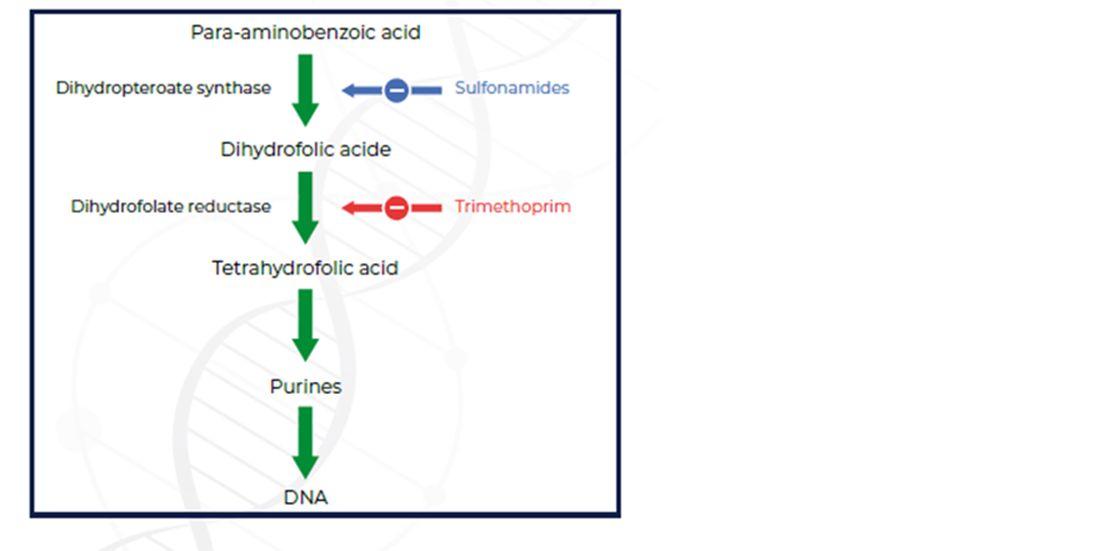
Sulfonamide and trimethoprim combinations act by targeting two sequential steps in the biosynthesis pathway for tetrahydrofolate (THF) as shown in Figure 1. The combined activity results in synergistic effects and increasing efficacy against different bacterial pathogens.
All sulfonamides have the same mechanism of action. Nevertheless, there are differences with respect to activity and pharmacokinetic behaviour at therapeutic concentrations.
Sulfonamide and trimethoprim - therapeutic use in pigs
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has categorised antibiotics for their practical use in animals. Sulfonamides and trimethoprim are considered as first line treatment options (Category D) and should be used for therapeutic purposes whenever possible.
The potentiating effect of sulfonamide / trimethoprim combinations is an important product advantage and can be used in different respects:
- to increase the efficacy of sulfonamides from bacteriostatic to bactericidal drugs
- to use the synergistic effect for treatment of low susceptible and/or resistant bacteria
- to reduce the incidence of resistance
- to broaden the antibacterial spectrum
Susceptibility of swine bacteria to sulfonamide / trimethoprim combinations
Susceptibility patterns of swine bacteria pathogens are ideally monitored over longer time periods to identify declines and changes in their sensitivity. In the Pan-European VetPath survey, the susceptibility against sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim as a sulfonamide/trimethoprim representative was tested (Table 1).
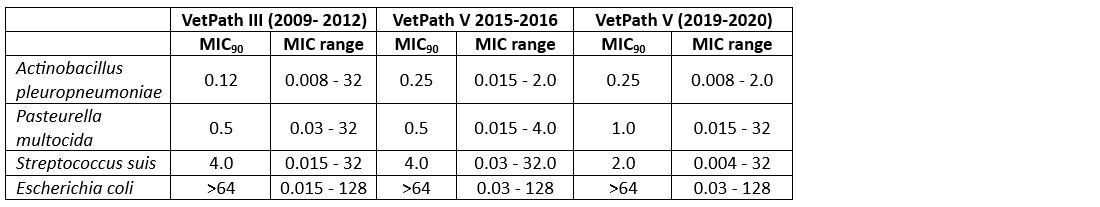
Over a period of 12 years, similar susceptibilities were determined with no trend in minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) changes. High susceptibilities were determined in the case of tested respiratory pathogens (A. pleuropneumoniae, P. multocida, S. suis). Low susceptibility was identified for Escherichia coli strains. The bacteria strains originated from eight different European countries.
The stable susceptibility of many bacteria species is one of the reasons for the high efficacy of sulfonamide/trimethoprim combination products in cases of treatment for a variety of bacterial infections in pigs. Their potent synergistic action prevents MIC increases long-term and the development of resistance.
Sulfonamides/trimethoprim - pharmacokinetics in pigs
Several pharmacokinetic studies in pigs have verified differences in the pharmacokinetic behaviour of sulfonamide/trimethoprim products at therapeutic concentrations.
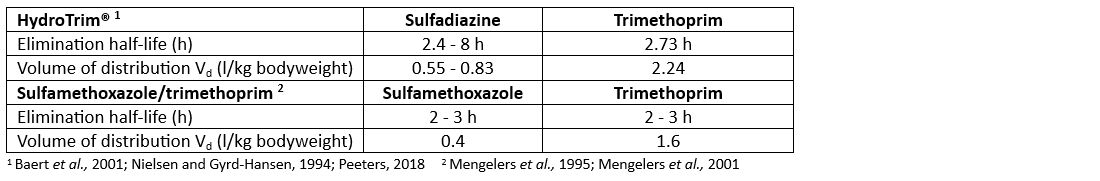
Sulfadiazine shows a longer elimination half-life which results in slower disappearance and higher and longer systemic availability in the target tissues in comparison to sulfamethoxazole. The higher distribution volume of the sulfadiazine/trimethoprim combination results in more intensive distribution into extravascular tissues in comparison to the sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim product.
Cornerstone of therapeutic use of HydroTrim and potentiated sulfonamides
- Potentiated sulfonamide products should be used as a first line treatment option to minimise the use of antimicrobials which are critically important in human medicine (quinolones; 3rd and 4th generation cephalosporines; polymyxins).
- The synergistic interaction of sulfonamides with trimethoprim potentiates their clinical efficacy and exhibits bactericidal activity against many bacterial pathogens.
- Pan-European MIC data confirms the consistent susceptibility of a variety of pig bacterial pathogens against potentiated sulfonamide products.
- Pharmacokinetic properties are in favour of HydroTrim sulfadiazine/trimethoprim. This justifies the therapeutic use of HydroTrim as first preference in pig farms vs. other sulfonamide/trimethoprim combinations.


