An analysis was made using intestinal health data from Aviapp® and treatment data collected over a 7-month period (January to July 2019) in 763 Belgian broiler flocks.
Among the 763 flocks, two different coccidiosis programs were applied through the period:
- 154 flocks used nicarbazin / narasin from day 1 until thinning (nicarbazin / narasin full)
- 609 flocks used nicarbazin / narasin until day 20/21 followed by Sacox® until thinning (nicarbazin / narasin - Sacox® shuttle)
The anticoccidial products were used at the registered dosages until thinning. As a standard practice, thinning took place at an average of 32 days and slaughter took place at an average age of 38 days. After thinning, all flocks received blank feed until slaughter.
Intestinal health monitoring included coccidiosis scoring (Johnson and Reid, 1970) and dysbacteriosis scoring (Teirlynck et al., 2011), performed on at least five birds per flock with an age range of 14 - 38 days.
Birds on the nicarbazin / narasin - Sacox® shuttle program showed lower average dysbacteriosis (0.46) and coccidiosis (0.76) scores in comparison to the nicarbazin / narasin full program (0.57 and 0.95, respectively), indicating better coccidiosis control in the nicarbazin / narasin - Sacox® shuttle program (Table 1).
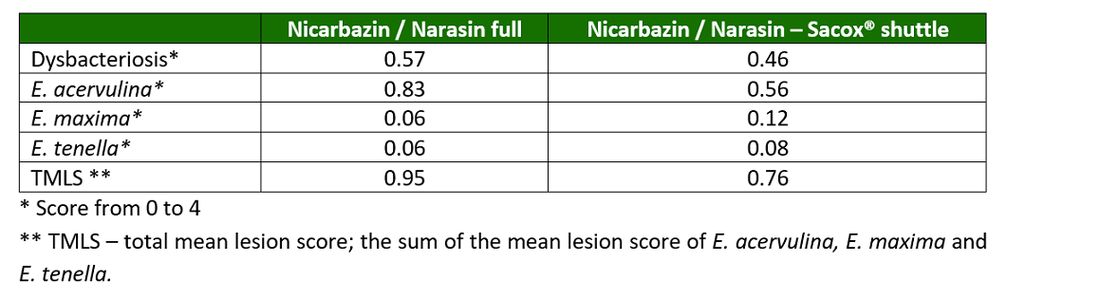
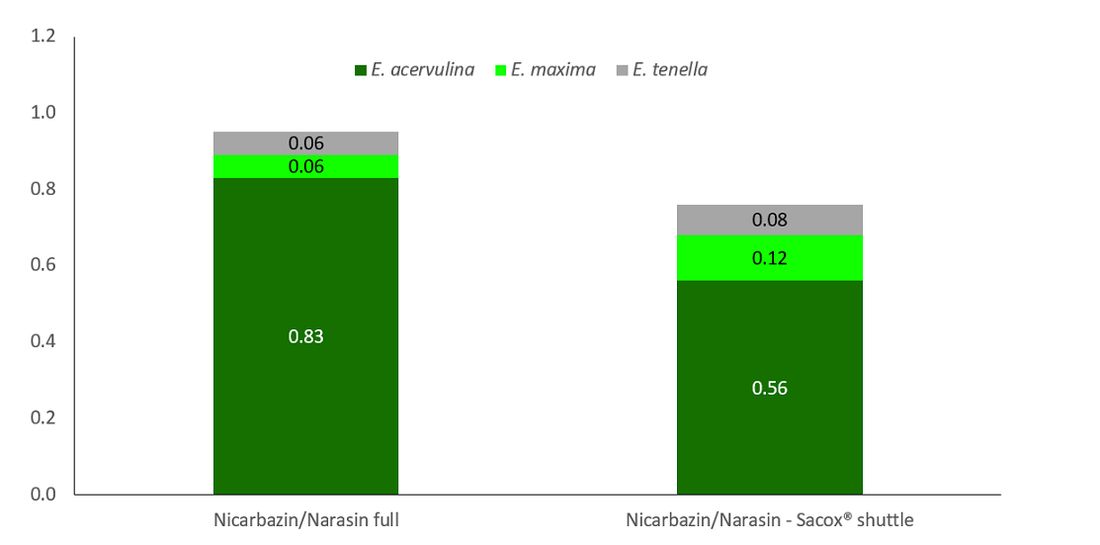
Eimeria acervulina was the main species diagnosed and was better controlled by the nicarbazin / narasin - Sacox® shuttle program (0.56 vs 0.83 for nicarbazin / narasin full; Figure 1).
In order to evaluate further differences between the different anticoccidial programs, the antimicrobial usage for enteric problems (in mg active/bird placed) was documented for each flock. The amount of antimicrobials used for enteric problems was lower in the flocks receiving the nicarbazin / narasin - Sacox® shuttle program (24.55 mg active/bird placed) compared to the flocks on the nicarbazin / narasin full program (28.33 mg active/bird placed; Table 2).

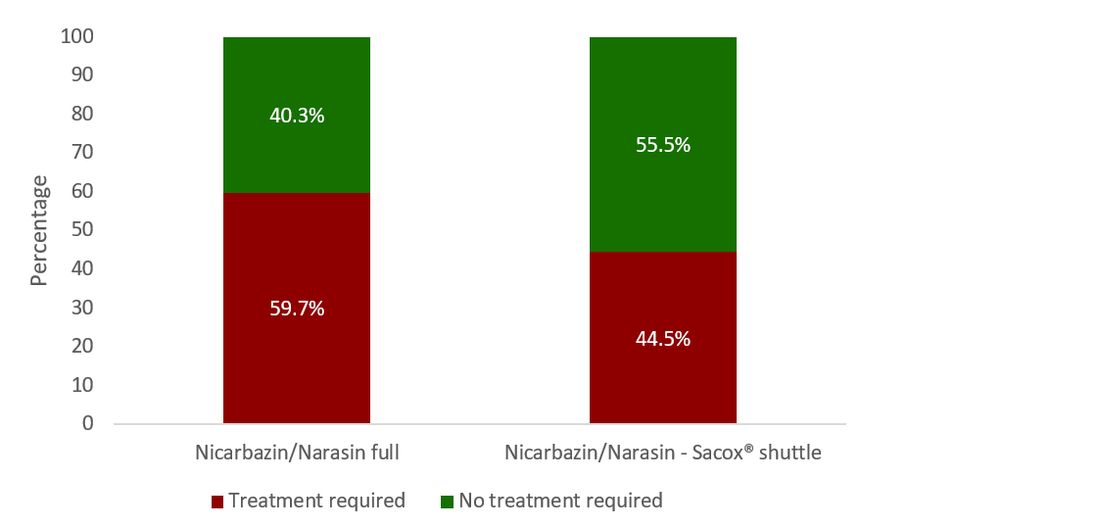
When looking at the percentage of flocks requiring enteric treatment (Figure 2), this was higher in the farms on the nicarbazin / narasin program than in the farms on the nicarbazin / narasin - Sacox® shuttle (59.7% vs 44.5%, respectively).
The analysis of data collected in Aviapp® supported the hypothesis that lower coccidiosis pressure (better coccidiosis control) has a positive impact on the amount of antimicrobial active used to treat enteric problems. Suboptimal coccidiosis control can be a driver for increased antimicrobial usage.
Aviapp® allows for easy and efficient data collection and processing, providing an excellent tool for poultry producers but also for veterinarians to follow-up health and performance.
References are available on request.



